Ozone in water treatment - World Ozone day 2022

Date: SEPTEMBER 16, 2022 | Author: DR AVINASH KADAM (Ph. D, IIT Bombay)(MD at Sugam Paryavaran Vikalp Pvt Ltd)
Ozone
Just over 34 years ago, scientists discovered an environmental crisis so terrifying it shocked the world into action. The image of the ozone hole over Antarctica – a widening rip in the very fabric of Earth’s sun-shielding stratosphere – was a symbol of destruction. Policies were quickly put in place to ban the offending chemicals, and so began the long, slow process of fixing the damage. In the decades since, ozone has taken a backseat in the minds of the public as fresh crises have arisen. Today we’re more likely to hear about the perils of climate change, plastic and urban smog. But the hole remains, and there are signs that ozone depletion cannot yet be ticked off.
In commemoration of Preservation of Ozone layer, every year September 16 has been calendar marked as International Day for the Preservation of the Ozone Layer (informally and simply called Ozone Day) by United Nation’s General assembly. This designation had been made on December 19, 2000, in commemoration of the date, in 1987, on which nations signed the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer.
On the other hand, this sensitization has overlooked other aspects of this molecule which is paramount. Ozone (O3), a gas discovered in the mid-nineteenth century, is a molecule consisting of three atoms of oxygen in a dynamically unstable structure due to the presence of mesomeric states. The gas is colorless, acrid in odour and explosive in liquid or solid form. It has a half-life of 40 min at 20°C and about 140 min at 0°C. Its basic function is to protect humans from harmful effects of UV radiation. Ozone occurs at less than 20 μg/m3 from the Earth's surface at concentrations that are perfectly compatible with life. It is a very strong disinfectant & oxidant. Any pathogen or contaminant that can be disinfected altered or removed via an oxidation process, will be affected by ozone. It is the strongest of all molecules available for disinfection.
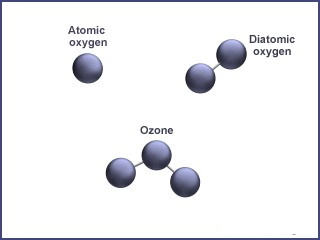
In water treatment ozone is more than twice as powerful as chlorine and acts 3000 times faster. Ozone can be used as a disinfectant deodorizer, detoxifier and a coagulant. Due to these properties ozone is widely used in air, water and waste water treatment in variety of applications.
What Ozone can Do?
Apart from its pivotal role in absorbing UV radiations and protecting the atmosphere from the potential danger of reaching these rays on earth, Ozone Technology finds its application in
- Water Treatment: Ozone has excellent disinfection and oxidative properties and is widely used in drinking water treatment. Mainly used in Bottled Water for complete elimination of chlorine treatment in raw water reduction in load on carbon filter and RO. Ozone kills all the living organisms almost instantly. Ozone provides a residual protection in the water. It improves the taste and the clarity of the water. It doesn't form any harmful by products. It is generated at the site and hence doesn't require any operator or chemical storage.
- Waste Water Treatment:
Disinfection: Ozone kills Bacteria and virus by cellular lyses and hence has greater role in water treatment.
Colour Removal: Ozone bleaches organic coloring matter ozone is a strong but natural bleaching agent good for whites as well as coloured clothes. Breaks bonds that holds soil and stains to the linen. Breaks down organic stains like oil and blood stains.
Odour Removal: Ozone oxidizes odour and taste causing compounds and hence potential application in Wastewater treatment and air treatment. Ozone is a strong oxidizer. It eliminates any odour causing bacteria and organics Eliminates the use of bleach hence no chlorine smell.
COD/BOD reduction: Ozone oxidizes COD and BOD of the chemical effluent. It is used in TEXTILE EFFLUENTS/ PAPER PULP EFFLUENTS/ PESTICIDES EFFLUENTS/ BULK DRUG INDUSTRIES/ PLATING EFFLUENTS/ TANNRIES/DAIRIES AND FOOD PRODUCTS/ Common Effluent Treatment Plants (CETPs).
Micro-flocculation: Ozone assists in micro-flocculation in the filters Oxidation of Inorganic Compounds: Ozone forms metal oxides which can be filtered. - Air Treatment: Gases may include organic chemicals such as olefins, fatty acids, ketones, nitrites, ester, amines and sulphur- bearing compounds. Ozone is mixed with the polluted air by means of an injection nozzle. Few seconds are enough to effectively oxidize the gaseous pollutants. It can also used in modern days HVAC system to get rid of VOCs and to ensure fresh air.
- Medical Healing: Ozone therapy has been utilized and extensively studied for many decades altogether. Its effects are proven, consistent and with minimal side effects. Medical O3, used to disinfect and treat disease, has been around for over 150 years. Although O3 has dangerous effects, yet researchers believe it has many therapeutic effects. Ozone is used for accelerated healing of wounds etc. Ozone has a capacity to oxidize organic compounds and has well-known toxic effects on the respiratory tract when present in smog. In medical use the gas produced from medical grade oxygen is administered in precise therapeutic doses, and never via inhalation, and advocates that it has excellent health benefits in dental caries, decrease blood cholesterol and stimulation of antioxidative responses, modifies oxygenation in resting muscle and is used in complementary treatment of hypoxic and ischemic syndromes.